Two inspiring UWTSD journeys
Today’s blog post features 2 inspiring UWTSD journeys, that show the power of creative and technical education in supporting and transforming peoples lives & futures.
Mia Harries is turning her passion for computer games into a creative career, growing in confidence and industry readiness through hands‑on learning, professional networking, and her long‑standing involvement with Yr Egin.
Meanwhile, Adam Moore has reshaped his career through UWTSD’s Digital Degree Apprenticeship in Computing, progressing from NHS data analyst to an emerging researcher developing AI tools that support clinical decision‑making. Together, their stories showcase how UWTSD empowers learners of all backgrounds to thrive, whether in the world of game design or Computer Science & groundbreaking healthcare innovation.
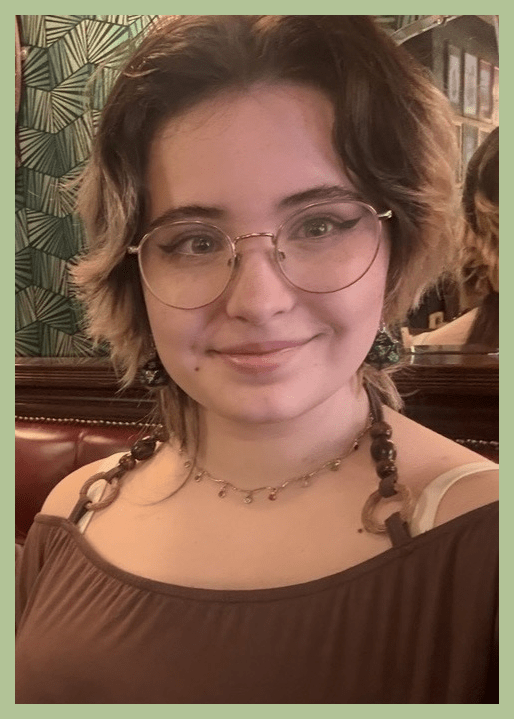
Mia Harries
> BA Computer Game Design
Mia Harries is turning a passion into a Creative Career. Mia’s time on UWTSD’s BA Computer Game Design course has helped her grow in confidence, creativity, and professional readiness.
Supported by a practical, industry‑focused learning environment, her wide-ranging course experience, combined with meaningful industry contact and her long-standing involvement with Yr Egin – where she has led workshops, built technical skills, and expanded her professional network, has shaped her into a confident emerging game designer. 🎮🎨
Mia now looks ahead to securing a role in a Welsh games studio while continuing freelance work, grateful for the skills, friendships, and guidance that have prepared her for the industry.
To read the full article, please click here:
* https://www.uwtsd.ac.uk/news/mia-harries-turns-passion-creative-career
To learn more about the University’s Computer Games Design Degree please click here.
\/
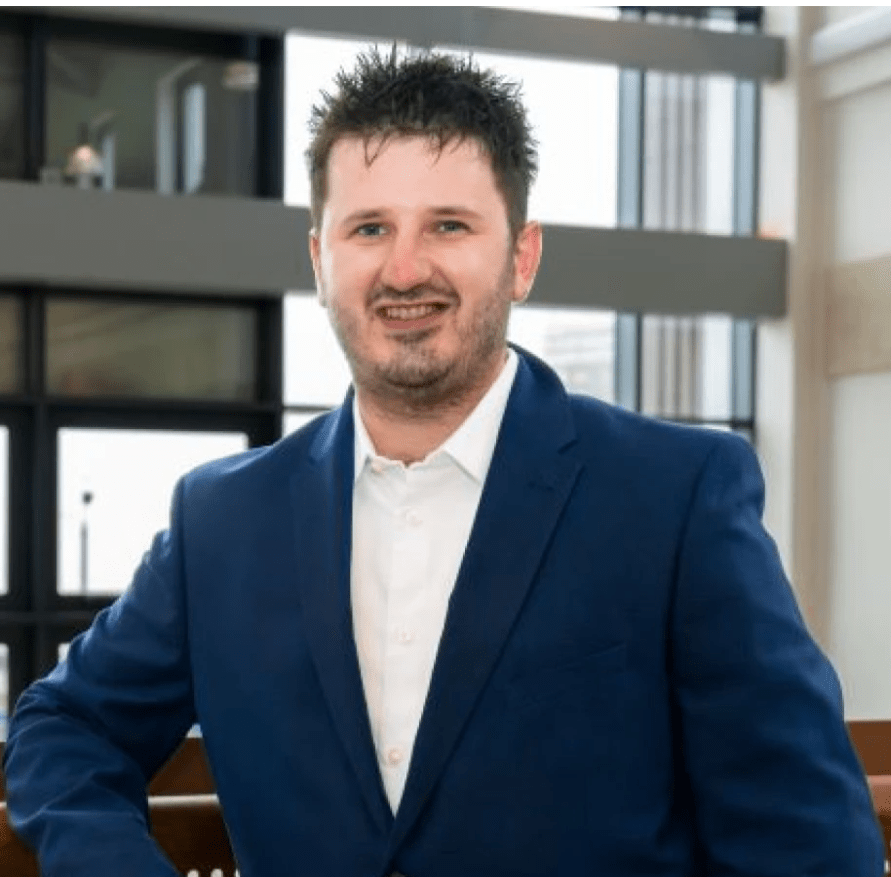
Adam Moore
> Digital Degree Apprenticeship
Adam Moore, a Data Scientist from Narberth, credits the University of Wales Trinity Saint David’s Digital Degree Apprenticeship in Computing (Data and Information Systems) with transforming his career and opening the door to advanced work in Artificial Intelligence (AI) and healthcare. While working at Hywel Dda University Health Board, Adam discovered a strong affinity for maths and data, and with encouragement from colleagues, he enrolled in the apprenticeship. This opportunity allowed him to study while working full‑time, supporting his family, and progressing professionally.
Throughout the four‑year programme, Adam successfully balanced academic study with full‑time employment, during which he got married, welcomed two children, and earned three promotions. The apprenticeship equipped him with the skills and confidence to excel in postgraduate study. Now undertaking doctoral research in AI and healthcare, he aims to contribute to innovations that enhance patient care and shape the future of digital health services.
Adam is a strong advocate for UWTSD’s apprenticeship route, praising it’s accessibility and the exceptional support offered by the university. UWTSD leaders emphasise how his journey reflects the programme’s impact across Wales, while colleagues at Hywel Dda describe him as a highly valued staff member whose AI work is already making a meaningful difference in clinical decision‑making.
“I want to play an active role in using AI to revolutionise healthcare and improve patient outcomes,” he said. “The apprenticeship was the foundation that made all of this possible.”
Adam continues to advocate for UWTSD’s Degree Apprenticeship route and encourages others to take advantage of the opportunity.
“It’s an incredible pathway for anyone looking to progress in their career,” he said. “It’s open to professionals of all ages who want to develop their skills and the support from the UWTSD team is exceptional.”
To read the full article, please click here:
* UWTSD Degree Apprenticeship Launches Pembrokeshire Data Scientist on Groundbreaking AI Career Path
To learn more about the University’s Degree Apprenticeships please click here:
* UWTSD Degree Apprenticeship programmes in Computing
~